Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tasaki, Yudai; Udagawa, Yutaka
JAEA-Data/Code 2024-012, 76 Pages, 2024/12
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been developing a fuel performance code, FEMAXI, to evaluate the behavior of LWR fuels under normal operation and transient conditions. In March 2019, FEMAXI-8, the first systematically validated and performance evaluated code, was released. Since then, the code has undergone various improvements. In parallel, since the 2000s, JAEA has been developing the RANNS module as a branch for design basis accident (DBA) analysis, with a particular emphasis on computational stability, so that fuel behavior can be tracked even for very steep transients, in this case mainly reactivity-initiated accidents (RIAs). The specific models include boiling heat transfer, fission gas release by grain boundary failure, and cladding failure determination based on fracture mechanics parameters, which are essential for predicting such transient behavior. In this report, prior to the release of RANNS, we present a description of the models for accident behavior analysis, the relationship with FEMAXI-8 in terms of the design and structure of the program, and the results of a large-scale validation using the extensive database of RIA experiments conducted and accumulated by JAEA, to evaluate the overall RIA analysis performance. The code will be made available to users as a packaged FEMAXI/RANNS, enabling them to analyze fuel behavior under various conditions. The model parameter sets determined through the above validation analyses are also presented in this report, and by referring to them, the analysis can be easily performed with almost no change in usability from the previously released FEMAXI-8.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; The University of Tokyo*
JAEA-Review 2024-021, 126 Pages, 2024/11
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2022. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2021, this report summarizes the research results of the "Study on water stopping, repair and stabilization of lower PCV by geopolymer, etc" conducted in FY2022. The present study aims to propose a construction method to stop jet deflectors by improved geopolymer and ultra-heavy muddy water, and to repair the lower part of the dry well. In addition, in order to increase the options for on-site construction in unknown situations such as deposition conditions, we will examine a wide range of construction outside the pedestal, and evaluate the feasibility of the construction method by the latest thermal flow simulation method.
Kim, M.; Malins, A.*; Machida, Masahiko; Yoshimura, Kazuya; Saito, Kimiaki; Yoshida, Hiroko*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi (Internet), 22(4), p.156 - 169, 2023/11
Dose reduction factor of a Japanese house is important information in the external exposure estimation of returning residents. In 2019, a total of 19 wooden houses were surveyed in Iitate Village and Namie Town using a gamma plotter that can continuously measure the air dose rate. In addition, the characteristics of the reduction factor were investigated from the measured air dose rate. In the vicinity of houses, uncontaminated areas exist underneath houses and, the ratio of paved surfaces such as asphalt roads is relatively high; furthermore, the pavement has a tendency for the radiation source to decay quickly. Therefore, the air dose rate near the house showed a relatively low value in common at all sites. Air dose rates above unpaved surfaces showed higher values and larger variations than those above paved surfaces within a radius of 50 m form the center of a house. The reduction factor was widely distributed even for one house, if the ratio of every air dose rate observed inside and outside the house is considered. It is suggested that a realistic reduction factor may not be obtained when the reduction factor is obtained based on the measured values at a small number of points that do not have the representativeness of the radiation field to be measured.
Ono, Ayato; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Sugita, Moe; Ueno, Tomoaki*; Horino, Koki*; Yamamoto, Kazami; Kinsho, Michikazu
JAEA-Technology 2022-036, 31 Pages, 2023/03
In the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), many electrical facilities such as power receiving equipment and power supply units are installed in experimental facilities such as the Nuclear Science Research Institute (NSRI) and the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC). However, some facilities have been in operation for more than half a century since they were manufactured, some have already been closed or deactivated, and others are still in operation while replacing parts and taking other aging measures. In these facilities, materials that were used because of their excellent properties at the time of manufacture are now designated as hazardous substances and require special management when disposed of. One of them is polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB). PCB were used in a very wide range of fields because of their stability against heat, high electrical insulation, and chemical resistance. However, it was found that PCB have persistent properties and may cause damage to human health and the living environment, and the government has enacted the "Act on Special Measures for Promotion of Proper Treatment of PCB Wastes (PCB Special Measures Law)" to promote reliable and proper disposal. JAEA has almost completed the excavation survey of high-concentration PCB waste and is in the process of excavating low-concentration PCB waste. However, there are still new relevant items to be discovered. This report summarizes and reports the knowledge necessary for identifying PCB waste and points to be noted when handling capacitors, etc., based on examples of actual disassembly and investigation work conducted on power supply units and other electrical equipment, such as capacitors attached to power supply units, etc.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; The University of Tokyo*
JAEA-Review 2022-062, 121 Pages, 2023/03
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2021. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2021, this report summarizes the research results of the "Study on water stopping, repair and stabilization of lower PCV by geopolymer, etc." conducted in FY2021. The present study aims to propose a construction method to stop jet deflectors by improved geopolymer and ultra-heavy muddy water, and to repair the lower part of the dry well. In addition, in order to increase the options for on-site construction in unknown situations such as deposition conditions, we will examine a wide range of construction outside the pedestal, and evaluate the feasibility of the construction method by the latest thermal flow simulation method. When widely constructed, fuel debris and deposits discharged out of the pedestal are coated with water stop and repair materials and become waste ...
Otani, Kyohei; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Kato, Chiaki
Zairyo To Kankyo, 71(2), p.40 - 45, 2022/02
The purpose of this study is to investigate the effect of oxygen concentration in the air on the corrosion rate of carbon steel in an air/solution alternating environment in the low oxygen concentration range and to clarify the corrosion rate and corrosion mechanism of carbon steel depending on the oxygen concentration in air by the mass change of specimens before and after the corrosion test and observing the iron rust layer formed on the surface of carbon steel. The corrosion rate increases with increasing oxygen concentration in the air, and the gradient of the corrosion rate decreases gradually. The maximum erosion depth increased with increasing oxygen concentration except for the case of 1% oxygen concentration, however, the maximum erosion depth for 1% oxygen concentration was larger than that for 5% air oxygen concentration.
Udagawa, Yutaka; Tasaki, Yudai
JAEA-Data/Code 2021-007, 56 Pages, 2021/07
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has released FEMAXI-8 in 2019 as the latest version of the fuel performance code FEMAXI, which has been developed to analyze thermal and mechanical behaviors of a single fuel rod in mainly normal operation conditions and anticipated transient conditions. This report summarizes a newly developed model to analyze intragranular fission gas behaviors considering size distribution of gas bubbles and their dynamics. While the intragranular fission gas behavior models implemented in the previous FEMAXI versions have supported only treating single bubble size for a given fuel element, the new model supports multiple gas groups according to their size and treats their dynamic behaviors, making the code more versatile. The model was first implemented as a general module that takes arbitrary number of bubble groups and spatial mesh division for a given fuel grain system. An interface module to connect the model to FEMAXI-8 was then developed so that it works as a 2 bubble groups model, which is the minimum configuration of the multi-grouped model to be operated with FEMAXI-8 at the minimum calculation cost. FEMAXI-8 with the new intragranular model was subjected to a systematic validation calculation against 144 irradiation test cases and recommended values for model parameters were determined so that the code makes reasonable predictions in terms of fuel center temperature, fission gas release, etc. under steady-state and power ramp conditions.
Okuno, Hiroshi; Sato, Sohei; Kawakami, Takeshi; Yamamoto, Kazuya; Tanaka, Tadao
Journal of Radiation Protection and Research, 46(2), p.66 - 79, 2021/06
The nuclear accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (NPS) of Tokyo Electric Power Company (TEPCO) was a typical one of the disastrous damages that induced evacuation of the residents around the NPS, which was triggered by the hugest earthquake and associated tsunami. This paper summarized early responses of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), especially of its Nuclear Emergency Assistance and Training Center (NEAT) to the off-site emergencies associated with the TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi NPS. The paper addressed activities of emergency preparedness of the NEAT before 2011 in relevant to the TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi NPS, the situation of the NEAT on March 11, 2011, and its early responses to the related off-site emergencies including those caused by the accident at the TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi NPS. The paper also discussed issues associated with complex disasters.
Asahi, Yuichi; Fujii, Keisuke*
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 97(2), p.86 - 92, 2021/02
The 5D gyrokinetic simulation data has been analyzed with the data-driven analysis methods. By defining an entropy-like quantity with singular values, we have quantitatively evaluated the randomness of the plasma state. We found that the randomness of plasma increases after the avalanche like transport and then gradually decrease. Since the decrease of the randomness is expected to be relevant to the phase space structure formation, we have developed a method to extract the phase space structures from the time series of 5D data. The relationship between the avalanche-like transport and phase space structures is discussed based on the contribution of each principal component to the energy transport.
Asahi, Yuichi; Fujii, Keisuke*; Heim, D. M.*; Maeyama, Shinya*; Garbet, X.*; Grandgirard, V.*; Sarazin, Y.*; Dif-Pradalier, G.*; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Yagi, Masatoshi*
Physics of Plasmas, 28(1), p.012304_1 - 012304_21, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:42.02(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)This article demonstrates a data compression technique for the time series of five dimensional distribution function data based on Principal Component Analysis (PCA). Phase space bases and corresponding coefficients are constructed by PCA in order to reduce the data size and the dimensionality. It is shown that about 83% of the variance of the original five dimensional distribution can be expressed with 64 components. This leads to the compression of the degrees of freedom from 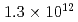 to
to 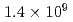 . One of the important findings - resulting from the detailed analysis of the contribution of each principal component to the energy flux - deals with avalanche events, which are found to be mostly driven by coherent structures in the phase space, indicating the key role of resonant particles.
. One of the important findings - resulting from the detailed analysis of the contribution of each principal component to the energy flux - deals with avalanche events, which are found to be mostly driven by coherent structures in the phase space, indicating the key role of resonant particles.
Fukahori, Tokio
JAEA-Conf 2020-001, p.17 - 20, 2020/12
After 9 years from the accident at TEPCO Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, the "on-site" research and development (R&D) situation has been changed into new phase. It can be considered from understanding to predicting by many direct and indirect measurements and analyses. In this presentation, nuclear data needs for 1F decommissioning are revisited according to these situation. The needs for accident evolution characteristics, criticality management, debris storage, waste management, etc. are considered with the view point of R&D on prediction what is going on and will be happened in each stage of decommissioning.
Nagao, Fumiya; Niizato, Tadafumi; Sasaki, Yoshito; Ito, Satomi; Watanabe, Takayoshi; Dohi, Terumi; Nakanishi, Takahiro; Sakuma, Kazuyuki; Hagiwara, Hiroki; Funaki, Hironori; et al.
JAEA-Research 2020-007, 249 Pages, 2020/10
The accident of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. occurred due to the Great East Japan Earthquake, Sanriku offshore earthquake, of 9.0 magnitude and the accompanying tsunami. As a result, large amount of radioactive materials was released into the environment. Under these circumstances, Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been conducting "Long-term Assessment of Transport of Radioactive Contaminants in the Environment of Fukushima" concerning radioactive materials released in environment, especially migration behavior of radioactive cesium since November 2012. This report is a summary of the research results that have been obtained in environmental dynamics research conducted by JAEA in Fukushima Prefecture.
Kawamura, Takuma; Idomura, Yasuhiro
Journal of Visualization, 23(4), p.695 - 706, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:5.80(Computer Science, Interdisciplinary Applications)An in-situ visualization system based on the particle-based volume rendering offers a highly scalable and flexible visual analytics environment based on multivariate volume rendering. Although it showed excellent computational performance on the conventional CPU platforms, accelerated computation on the latest many core platforms revealed performance bottlenecks related to a function parser and particles I/O. In this paper, we develop a new SIMD-aware function parser and an asynchronous data I/O method based on task-based thread parallelization. Numerical experiments on the Oakforest-PACS, which consists of 8208 Intel Xeon Phi7250 (Knights Landing) processors, demonstrate an order of magnitude speedup with keeping improved strong scaling up to  100 k cores.
100 k cores.
Yamashita, Takuya; Sawada, Noriyoshi*
JAEA-Research 2019-010, 227 Pages, 2020/03
In order to support the decontamination activities proceeded by the national government and municipalities in terms of technology, we have developed a simulation system "RESET" which predicts the effect of decontamination. We also developed a "two-component model" for the purpose of predicting long-term changes in the air dose rate. We use these tools to perform decontamination simulation and predictive analysis of the air dose rate after decontamination, and provide information to the national government and municipalities aiming for reconstruction. In this report, the verification result of the prediction methods implemented using actual measurement data obtained in the "Decontamination model demonstration project in difficult-to-return zone" and "Survey result on transition of air dose rate after decontamination model demonstration project" conducted by Ministry of the Environment. In addition, the decontamination simulation conducted for the entire difficult-to-return area and the results of future prediction of the air dose rate after decontamination are shown.
Udagawa, Yutaka; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki; Amaya, Masaki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 56(12), p.1063 - 1072, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:58.28(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Udagawa, Yutaka; Amaya, Masaki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 56(6), p.461 - 470, 2019/06
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:69.57(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Udagawa, Yutaka; Yamauchi, Akihiro*; Kitano, Koji*; Amaya, Masaki
JAEA-Data/Code 2018-016, 79 Pages, 2019/01
FEMAXI-8 is the latest version of the fuel performance code FEMAXI developed by JAEA. A systematic validation work has been achieved against 144 irradiation test cases, after many efforts have been made, in development of new models, improvements in existing models and the code structure, bug-fixes, construction of irradiation-tests database and other infrastructures.
Akagi, Yosuke*; Kato, Hiroyasu*; Tachi, Yukio; Sakamoto, Hiroyuki*
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 5, p.233 - 236, 2018/11
A large amount of radioactive contaminated concrete will be generated from the decommissioning in the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant (NPP). For developing the plans of decommissioning and waste management including decontamination and disposal, it is important to estimate radionuclides inventory and concentration distribution in the concrete materials. In this study, effective diffusivities (De) and distribution coefficients (Kd) of HTO, Cs, I and U in OPC mortar were measured by through-diffusion and batch sorption experiments. De values derived were in the sequence of HTO, I, Cs, U, implying that cation exclusion effects may be important mechanisms in OPC mortar. Kd values derived by batch tests were higher by more than one order of magnitude than the diffusion-derived Kd values, indicating that crushing of samples had a strong influence on sorption. Diffusion and sorption mechanisms in OPC mortar were evaluated to predict the penetration behavior of these radionuclides.
Nuclear Emergency Assistance and Training Center
JAEA-Review 2017-011, 54 Pages, 2017/07
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) is a designated public institution under the Disaster Countermeasures Basic Act and under the Armed Attack Situations Response Act. Based on these Acts, the JAEA has the responsibility of providing technical support to the national and some local governments in case of a nuclear incident. In case of a nuclear emergency, the Nuclear Emergency Assistance and Training Center (NEAT) dispatches experts of JAEA, supplies the governments with emergency equipment, and gives them technical advice and information. In normal time, NEAT provides various drills/exercises and training courses to nuclear emergency responders. In FY2015, the NEAT accomplished the following tasks: (1) Improvement of hardware and software for technical support activities (2) Human resource development, exercise and training of nuclear emergency responders ; (3) Researches on nuclear emergency preparedness and response, and dissemination of useful information for emergency responders; (4) Arrangements for technical support for aerial monitoring; and (5) Technical contributions to Asian countries on nuclear emergency preparedness and response.
Mukai, Yasunobu; Nakamichi, Hideo; Kobayashi, Daisuke; Nishimura, Kazuaki; Fujisaku, Sakae; Tanaka, Hideki; Isomae, Hidemi; Nakamura, Hironobu; Kurita, Tsutomu; Iida, Masayoshi*; et al.
Proceedings of 2017 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP 2017) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2017/04
TRP has stored the plutonium in solution state for long-term since the last PCDF operation in 2007 was finished. After the great east Japan earthquake in 2011, JAEA had investigated the risk against potential hazard of these solutions which might lead to make hydrogen explosion and/or boiling of the solution accidents with the release of radioactive materials to the public when blackout. To reduce the risk for storing Pu solution (about 640 kg Pu), JAEA planned to perform the process operation for the solidification and stabilization of the solution by converted into MOX powder at PCDF in 2013. In order to perform PCDF operation without adaption of new safety regulation, JAEA conducted several safety measures such as emergency safety countermeasures, necessary security and safeguards (3S) measures with understanding of NRA. As a result, the PCDF operation had stared on 28th April, 2014, and successfully completed to convert MOX powder on 3rd August, 2016 for about 2 years as planned.